What Natural Resources Can Be Found Outside of the United States?

 | |
| Continent | North America |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 38°00′00″Northward 97°00′00″West / 38.000°N 97.000°W / 38.000; -97.000 |
| Area | Ranked 3rd/quaternary |
| • Total | 9,826,675 km2 (three,794,100 sq mi) |
| • Country | 93.24% |
| • Water | 6.76% |
| Coastline | 19,920 km (12,380 mi) |
| Borders | Canada: 8,864 km (5,508 mi) Mexico: 3,327 km (ii,067 mi) |
| Highest point | Denali 6,190.5 m (xx,310 ft) |
| Everyman point | Badwater Bowl, −85 m (−279 ft) |
| Longest river | Missouri River, 3,767 km (2,341 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lake Superior 58,000 kmtwo (22,394 sq mi) |
| Climate | Diverse: Ranges from Temperate in the North to Tropical in the far south. W: mostly semi-arid to desert, Mountains: alpine, Northeast: humid continental, Southeast: boiling subtropical, Coast of California: Mediterranean, Pacific Northwest: cool temperate oceanic, Alaska: more often than not subarctic, Hawaii, Due south Florida, and the territories: tropical |
| Terrain | Vast fundamental plain, Interior Highlands and low mountains in Midwest, mountains and valleys in the mid-s, coastal flatland near the Gulf and Atlantic coasts, consummate with mangrove forests and temperate, subtropical, and tropical laurel forest and jungle, canyons, basins, plateus, and mountains in westward, hills and low mountains in east; intermittent hilly and mountainous regions in Peachy Plains, with occasional badland topography; rugged mountains and broad river valleys in Alaska; rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii and the territories |
| Natural resources | coal, copper, atomic number 82, molybdenum, phosphates, rare earth elements, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber, arable country |
| Natural hazards | tsunamis; volcanoes; earthquake activity around Pacific Bowl; hurricanes along the Atlantic and Gulf of United mexican states coasts; tornadoes in the Midwest and Southeast; mud slides in California; forest fires in the w; flooding; permafrost in northern Alaska |
| Environmental issues | severe water shortages, air pollution resulting in acid rain in both the United states of america and Canada |
| Exclusive economic zone | 11,351,000 km2 (four,383,000 sq mi) |
The term "United States", when used in the geographical sense, is the contiguous U.s., the state of Alaska, the isle state of Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.Southward. Virgin Islands, Guam, and American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions.[one] The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, The Bahamas, and other countries,[notation 2] in addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world'due south longest bi-national land border.
Area [edit]
From 1989 through 1996, the total surface area of the US was listed as nine,372,610 kmtwo (3,618,780 sq mi) (land + inland water but). The listed total expanse changed to ix,629,091 kmii (3,717,813 sq mi) in 1997 (Peachy Lakes area and coastal waters added), to nine,631,418 km2 (3,718,711 sq mi) in 2004, to 9,631,420 kmii (three,718,710 sq mi) in 2006, and to ix,826,630 km2 (3,794,080 sq mi) in 2007 (territorial waters added). Currently, the CIA Globe Factbook gives 9,826,675 km2 (three,794,100 sq mi),[7] the Un Statistics Division gives 9,629,091 km2 (3,717,813 sq mi),[8] and the Encyclopædia Britannica gives nine,522,055 kmii (three,676,486 sq mi) (Nifty Lakes area included simply not littoral waters).[9] These sources consider only the 50 states and the Federal Commune, and exclude overseas territories. The US has the 2nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 11,351,000 kmtwo (4,383,000 sq mi).
By total area (water equally well every bit land), the United states is either slightly larger or smaller than the People'southward Republic of Red china, making it the world's third or fourth largest state. China and the United states of america are smaller than Russia and Canada in total expanse, but are larger than Brazil. By land surface area only (exclusive of waters), the United States is the world'due south tertiary largest country, after Russian federation and China, with Canada in 4th. Whether the US or Cathay is the third largest country by full area depends on two factors: (1) The validity of China'due south merits on Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract. Both these territories are besides claimed by India, so are non counted; and (2) How US calculates its own surface area. Since the initial publishing of the World Factbook, the CIA has updated the total area of United States a number of times.[10]
General characteristics [edit]

A satellite blended image of the face-to-face The states. Temperate and Subtropical forests, of a deciduous, coniferous, broadleaved evergreen, and mixed vegetation, too equally grasslands, montane forests, and croplands prevail in the eastward, transitioning to prairies (semi-arid steppe), boreal forests, and the Rockies in the west, and deserts in the southwest. In the northeast, the coasts of the Great Lakes and Atlantic seaboard host much of the land's population.

A satellite blended image of the state of Hawaii. Volcanoes prevail on the Large Island. The islands take rugged coastlines, sandy beaches and a tropical environment, although temperatures and humidity tend to be less farthermost considering of most-constant trade winds from the eastward.
The The states shares state borders with Canada (to the north) and Mexico (to the south), and a territorial water border with Russian federation in the northwest, and ii territorial water borders in the southeast between Florida and Cuba, and Florida and the Bahamas. The contiguous forty-8 states are otherwise bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the westward, the Atlantic Ocean on the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Alaska borders the Pacific Sea to the south and southwest, the Bering Strait to the west, and the Arctic Ocean to the north, while Hawaii lies far to the southwest of the mainland in the Pacific Ocean.
40-viii of united states are in the single region betwixt Canada and Mexico; this grouping is referred to, with varying precision and formality, as the face-to-face Usa, and every bit the Lower 48. Alaska, which is included in the term continental United States, is located at the northwestern end of North America.
The capital city, Washington, Commune of Columbia, is a federal district located on state donated past the land of Maryland. (Virginia had also donated country, but it was returned in 1849.) The Us besides has overseas territories (Insular areas) with varying levels of autonomy and organization: in the Caribbean the territories of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands (formerly the Danish Virgin Islands, purchased by the The states at the beginning of WW2), and in the Pacific the inhabited territories of American Samoa, Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, along with a number of uninhabited island territories. Some of the territories acquired were a part of Usa imperialism, or to gain access to the east.
Nearly all of the United states of america is in the northern hemisphere — the exceptions are American Samoa and Jarvis Isle, which are in the southern hemisphere.[11]
Physiographic divisions [edit]

The eastern Usa has a varied topography. A broad, flat coastal plain lines the Atlantic and Gulf shores from the Texas-Mexico border to New York City, and includes the Florida peninsula. This wide littoral plain and bulwark islands brand up the widest and longest beaches in the United States, much of it composed of soft, white sands. The Florida Keys are a string of coral islands that reach the southernmost city on the United states of america mainland (Key Westward). Areas further inland feature rolling hills, mountains, and a diverse drove of temperate and subtropical moist and wet forests. Parts of interior Florida and South Carolina are too home to sand-hill communities. The Appalachian Mountains form a line of low mountains separating the eastern seaboard from the Cracking Lakes and the Mississippi Basin. New England features rocky seacoasts and rugged mountains with peaks up to 6200 feet and valleys dotted with rivers and streams. Offshore Islands dot the Atlantic and Gulf coasts. A recent global remote sensing assay suggested that at that place were half-dozen,622 km² of tidal flats in the Usa, making it the 4th ranked country in terms of tidal flat expanse.[12]
The 5 Corking Lakes are located in the n-key portion of the country, 4 of them forming function of the edge with Canada, simply Lake Michigan situated entirely within United States. The southeast The states, mostly stretching from the Ohio River on due south, includes a variety of warm temperate and subtropical moist and wet forests, equally well as warm temperate and subtropical dry forests nearer the Smashing Plains in the westward of the region. Westward of the Appalachians lies the lush Mississippi River basin and 2 large eastern tributaries, the Ohio River and the Tennessee River. The Ohio and Tennessee Valleys and the Midwest consist largely of rolling hills, interior highlands and small mountains, jungly marsh and swampland well-nigh the Ohio River, and productive farmland, stretching southward to the Gulf Coast. The Midwest also has a vast amount of cavern systems.
The Great Plains lie west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains. A big portion of the country's agricultural products are grown in the Dandy Plains. Before their general conversion to farmland, the Slap-up Plains were noted for their extensive grasslands, from tallgrass prairie in the eastern plains to shortgrass steppe in the western Loftier Plains. Elevation rises gradually from less than a few hundred feet near the Mississippi River to more than than a mile high in the High Plains. The by and large low relief of the plains is cleaved in several places, almost notably in the Ozark and Ouachita Mountains, which form the U.Southward. Interior Highlands, the merely major mountainous region between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains.[xiii] [14]
The Not bad Plains come to an precipitous end at the Rocky Mountains. The Rocky Mountains form a large portion of the Western U.S., entering from Canada and stretching nearly to Mexico. The Rocky Mount region is the highest region of the United states by average peak. The Rocky Mountains mostly contain adequately mild slopes and wider peaks compared to some of the other peachy mountain ranges, with a few exceptions (such every bit the Teton Mountains in Wyoming and the Sawatch Range in Colorado). The highest peaks of the Rockies are found in Colorado, the tallest peak being Mount Elbert at 14,440 ft (4,400 m). In add-on, instead of being one generally continuous and solid mountain range, information technology is cleaved upwards into a number of smaller, intermittent mountain ranges, forming a large series of basins and valleys.
Westward of the Rocky Mountains lies the Intermontane Plateaus (also known as the Intermountain W), a large, arid desert lying betwixt the Rockies and the Cascades and Sierra Nevada ranges. The big southern portion, known as the Great Bowl, consists of common salt flats, drainage basins, and many pocket-size north–s mount ranges. The Southwest is predominantly a low-lying desert region. A portion known equally the Colorado Plateau, centered around the Four Corners region, is considered to have some of the about spectacular scenery in the world. Information technology is accentuated in such national parks as Grand Canyon, Arches, Mesa Verde and Bryce Canyon, among others. Other smaller Intermontane areas include the Columbia Plateau covering eastern Washington, western Idaho and northeast Oregon and the Snake River Plain in Southern Idaho.

The Grand Canyon from Moran Point. The Grand Canyon is among the most famous locations in the land.
The Intermontane Plateaus come up to an terminate at the Cascade Range and the Sierra Nevada. The Cascades consist of largely intermittent, volcanic mountains, many rise prominently from the surrounding landscape. The Sierra Nevada, farther due south, is a loftier, rugged, and dense mountain range. It contains the highest point in the face-to-face 48 states, Mount Whitney (14,505 ft or iv,421 m). It is located at the purlieus betwixt California's Inyo and Tulare counties, just 84.6 mi or 136.2 km west-northwest of the lowest point in North America at the Badwater Basin in Death Valley National Park at 279 ft or 85 m below sea level.[15]
These areas incorporate some spectacular scenery as well, as evidenced past such national parks as Yosemite and Mountain Rainier. West of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada is a series of valleys, such as the Central Valley in California and the Willamette Valley in Oregon. Along the coast is a series of low mountain ranges known equally the Pacific Declension Ranges.
Alaska contains some of the nigh dramatic scenery in the country. Tall, prominent mountain ranges rise upward sharply from broad, apartment tundra plains. On the islands off the due south and southwest coast are many volcanoes. Hawaii, far to the southward of Alaska in the Pacific Ocean, is a concatenation of tropical, volcanic islands, popular as a tourist destination for many from East Asia and the mainland The states.
The territories of Puerto Rico and the U.Southward. Virgin Islands encompass a number of tropical isles in the northeastern Caribbean Body of water. In the Pacific Ocean the territories of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands occupy the limestone and volcanic isles of the Mariana archipelago, and American Samoa (the only populated US territory in the southern hemisphere) encompasses volcanic peaks and coral atolls in the eastern function of the Samoan Islands concatenation.[annotation 3]
Physiographic regions [edit]

A physiographical map of the contiguous 48 states of the U.South. The map indicates the age of the exposed surface too as the type of terrain.
The geography of the United States varies across its immense area. Inside the continental U.S., eight distinct physiographic divisions exist, though each is composed of several smaller physiographic subdivisions.[16] These major divisions are:
- Laurentian Upland – function of the Canadian Shield that extends into the northern U.s. Great Lakes area.
- Atlantic Plain – the coastal regions of the eastern and southern parts includes the continental shelf, the Atlantic Coast and the Gulf Coast.
- Appalachian Highlands – lying on the eastern side of the U.s., it includes the Appalachian Mountains, the Watchung Mountains, the Adirondacks and New England province originally containing the Great Eastern Forest, a stretch of mixed temperature and subtropical montane forests, some of which are rainforests.
- Interior Plains – part of the interior continental U.s., it includes the Bully Plains, as well equally a number of highland and mountainous regions, like the Black Hills, dense cave systems, painted hills and badland features.
- Interior Highlands – also part of the interior continental The states, this partition includes the Ozark Plateau, the Ouachita Mountains, and other smaller mountain systems. This region is located largely in the warm temperate/subtropical moist and dry out forest biomes.
- Rocky Mountain System – one co-operative of the Cordilleran system lying far inland in the western states.
- Intermontane Plateaus – also divided into the Columbia Plateau, the Colorado Plateau and the Bowl and Range Province, it is a system of plateaus, basins, ranges and gorges betwixt the Rocky and Pacific Mount Systems. Information technology is the setting for the G Canyon, the Great Basin and Decease Valley.
- Pacific Mountain System – the coastal mountain ranges and features in the westward coast of the United states.

Much of the central United States is covered past relatively flat, arable state. This aerial photo was taken over northern Ohio.
The Atlantic coast of the United states is low, with minor exceptions. The Appalachian Highland owes its oblique northeast–southwest trend to crustal deformations which in very early geological time gave a commencement to what later came to be the Appalachian mountain system. This organization had its climax of deformation so long agone (probably in Permian time) that it has since then been very generally reduced to moderate or low relief. Information technology owes its nowadays-day altitude either to renewed elevations along the before lines or to the survival of the most resistant rocks as residual mountains. The oblique trend of this coast would be even more pronounced just for a comparatively modern crustal movement, causing a depression in the northeast resulting in an encroachment of the sea upon the land. Additionally, the southeastern department has undergone an elevation resulting in the advance of the land upon the ocean.
While the Atlantic coast is relatively low, the Pacific coast is, with few exceptions, hilly or mountainous. This coast has been divers chiefly by geologically recent crustal deformations, and hence nonetheless preserves a greater relief than that of the Atlantic. The low Atlantic declension and the hilly or mountainous Pacific coast foreshadow the leading features in the distribution of mountains within the United States.
The east coast Appalachian system, originally forest covered, is relatively depression and narrow and is bordered on the southeast and southward by an important coastal plain. The Cordilleran arrangement on the western side of the continent is lofty, broad and complicated having two branches, the Rocky Mountain System and the Pacific Mountain Organization. In between these mount systems lie the Intermontaine Plateaus. Both the Columbia River and Colorado River rise far inland near the easternmost members of the Cordilleran system, and flow through plateaus and intermontaine basins to the ocean. Heavy forests cover the northwest declension, only elsewhere trees are plant only on the higher ranges below the Alpine region. The intermontane valleys, plateaus and basins range from treeless to desert with the most arid region existence in the southwest.
The Laurentian Highlands, the Interior Plains and the Interior Highlands lie betwixt the two coasts, stretching from the Gulf of United mexican states northward, far beyond the national boundary, to the Arctic Bounding main. The central plains are divided by a hardly perceptible elevation of country into a Canadian and a United states portion. It is from the United States side, that the great Mississippi system discharges southward to the Gulf of Mexico. The upper Mississippi and some of the Ohio bowl is the semi-arid prairie region, with copse originally simply along the watercourses. The uplands towards the Appalachians were included in the great eastern forested area, while the western part of the plains has so dry a climate that its native establish life is scanty, and in the south it is practically arid.
Elevation extremes:
- Everyman point: Decease Valley, Inyo County, California −280 ft (−85.3 m)
- Highest point: Denali, Denali Borough, Alaska 20,310 ft (half-dozen,190.5 m)
Climate [edit]

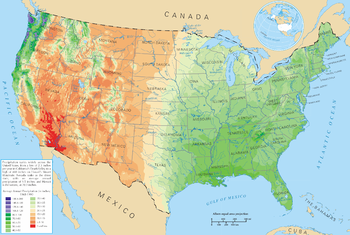
A map of average precipitation across the contiguous U.s..
Due to its large size and wide range of geographic features, the United States contains examples of most every global climate. The climate is subtropical in the Southern The states, tropical in Hawaii and southern Florida, polar in Alaska, semiarid in the Great Plains westward of the 100th meridian, Mediterranean in coastal California and barren in the Great Basin and the Southwest. Its comparatively favorable agricultural climate contributed (in part) to the state's ascension equally a world power, with exceptional severe drought in the major agronomical regions, a full general lack of widespread flooding, and a mainly temperate climate that receives acceptable precipitation.
The main influence on U.South. weather is the polar jet stream which migrates northward into Canada in the summer months, and so southward into the Us in the wintertime months. The jet stream brings in large low force per unit area systems from the northern Pacific Ocean that enter the US mainland over the Pacific Northwest. The Cascade Range, Sierra Nevada, and Rocky Mountains option up most of the moisture from these systems as they move east. Greatly diminished by the time they attain the High Plains, much of the wet has been sapped past the orographic outcome every bit information technology is forced over several mountain ranges.
Once information technology moves over the Dandy Plains, uninterrupted flat land allows it to reorganize and can pb to major clashes of air masses. In addition, moisture from the Gulf of Mexico is often drawn northward. When combined with a powerful jet stream, this can lead to trigger-happy thunderstorms, particularly during spring and summer. Sometimes during winter these storms can combine with another depression pressure organisation as they motion upward the East Declension and into the Atlantic Ocean, where they intensify rapidly. These storms are known every bit Nor'easters and oftentimes bring widespread, heavy rain, wind, and snowfall to New England. The uninterrupted grasslands of the Nifty Plains also lead to some of the almost extreme climate swings in the world. Temperatures can rise or drop quickly and winds can be extreme, and the flow of heat waves or Arctic air masses often accelerate uninterrupted through the plains.
The Keen Basin and Columbia Plateau (the Intermontane Plateaus) are arid or semiarid regions that lie in the rain shadow of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada. Precipitation averages less than xv inches (38 cm). The Southwest is a hot desert, with temperatures exceeding 100 °F (37.8 °C) for several weeks at a time in summer. The Southwest and the Great Basin are too afflicted by the monsoon from the Gulf of California from July to September, which brings localized but ofttimes severe thunderstorms to the region.
Much of California consists of a Mediterranean climate, with sometimes excessive rainfall from Oct–Apr and nearly no rain the rest of the yr. In the Pacific Northwest rain falls year-round, but is much heavier during winter and spring. The mountains of the west receive abundant precipitation and very heavy snowfall. The Cascades are one of the snowiest places in the world, with some places averaging over 600 inches (1,524 cm) of snow annually, just the lower elevations closer to the coast receive very little snow.
Florida has a subtropical climate in the northern part of the country and a tropical climate in the southern part of the land. Summers are wet and winters are dry in Florida. Annually much of Florida, as well as the deep southern states, are frost-free. The balmy winters of Florida let a massive tropical fruit manufacture to thrive in the central part of the state, making the US second to merely Brazil in citrus product in the world.
Another significant (just localized) weather effect is lake-effect snow that falls south and eastward of the Great Lakes, peculiarly in the hilly portions of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and on the Tug Hill Plateau in New York. The lake effect dumped well over 5 feet (1.52 m) of snowfall in the area of Buffalo, New York throughout the 2006-2007 winter. The Wasatch Front and Wasatch Range in Utah can also receive significant lake outcome accumulations from the Corking Common salt Lake.
Extremes [edit]
In northern Alaska, tundra and chill atmospheric condition predominate, where the temperature has fallen as low as −80 °F (−62.ii °C).[17] On the other end of the spectrum, Death Valley, California one time reached 134 °F (56.vii °C), the highest temperature ever recorded on Earth.[eighteen] [19]
On average, the mountains of the western states receive the highest levels of snowfall on World. The greatest annual snowfall level is at Mount Rainier in Washington, at 692 inches (1,758 cm); the tape there was 1,122 inches (2,850 cm) in the wintertime of 1971–72. This tape was broken by the Mt. Baker Ski Area in northwestern Washington which reported 1,140 inches (2,896 cm) of snowfall for the 1998-99 snowfall season. Other places with pregnant snow outside the Pour Range are the Wasatch Mountains in Utah, the San Juan Mountains in Colorado, and the Sierra Nevada in California.

In the eastward, the region nigh the Nifty Lakes and the mountains of the Northeast receive the almost snow, although such snowfall levels exercise not well-nigh snowfall levels in the western United States. Along the northwestern Pacific coast, rainfall is greater than anywhere else in the continental U.S., with Quinault Rainforest in Washington having an average of 137 inches (348 cm).[21] Hawaii receives even more, with 404 inches (ane,026 cm) measured annually in the Big Bog, in Maui.[22] Pago Pago Harbor in American Samoa is the rainiest harbor in the earth (because of the 523 meter Rainmaker Mount).[20] The Mojave Desert, in the southwest, is home to the driest locale in the U.S. Yuma, Arizona, has an average of ii.63 inches (6.seven cm) of precipitation each yr.[23]
In central portions of the U.S., tornadoes are more common than anywhere else on Earth[24] and touch down about ordinarily in the jump and summer. Deadly and destructive hurricanes occur almost every twelvemonth along the Atlantic seaboard and the Gulf of Mexico. The Appalachian region and the Midwest experience the worst floods, though virtually no area in the U.S. is allowed to flooding. The Southwest has the worst droughts; i is thought to have lasted over 500 years and to have hurt Ancestral Pueblo peoples.[25] The West is afflicted by large wildfires each year.
Natural disasters [edit]
The United States is affected by a multifariousness of natural disasters yearly. Although drought is rare, it has occasionally caused major disruption, such equally during the Dust Bowl (1931–1942). Farmland failed throughout the Plains, entire regions were about depopulated, and dust storms ravaged the land.

Tornadoes and hurricanes [edit]
The Peachy Plains and Midwest, due to the contrasting air masses, see frequent severe thunderstorms and tornado outbreaks during bound and summertime with around 1,000 tornadoes occurring each year.[26] The strip of country from north Texas north to Kansas and Nebraska and due east into Tennessee is known equally Tornado Alley, where many houses have tornado shelters and many towns accept tornado sirens due to the very frequent tornado formations in the region.
Hurricanes are another natural disaster institute in the US, which can striking anywhere along the Gulf Declension or the Atlantic Coast besides as Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. Peculiarly at chance are the central and southern Texas coasts, the area from southeastern Louisiana east to the Florida Panhandle, peninsular Florida, and the Outer Banks of North Carolina, although whatsoever portion of the coast could exist struck. The U.Due south. territories and possessions in the Caribbean area, such as Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, are also vulnerable to hurricanes due to their location in the Caribbean Sea.
Hurricane season runs from June ane to November xxx, with a peak from mid-August through early October. Some of the more devastating hurricanes take included the Galveston Hurricane of 1900, Hurricane Andrew in 1992, Hurricane Katrina in 2005, and Hurricane Harvey and Hurricane Maria in 2017.
Hurricanes (known equally cyclones in the Pacific Ocean) fail to landfall on the Pacific Coast of the U.s.a. due to water temperatures being too cool to sustain them. Nonetheless, the remnants of tropical cyclones from the Eastern Pacific occasionally impact the western United States, bringing moderate to heavy rainfall.

Flooding [edit]
Occasional severe flooding is experienced. In that location was the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927, the Slap-up Flood of 1993, and widespread flooding and mudslides caused by the 1982–83 El Niño consequence in the western Us. Flooding is still prevalent, by and large on the Eastern Coast, during hurricanes or other inclement weather condition, for case in 2012, when Hurricane Sandy devastated the region. Localized flooding can, withal, occur anywhere, and mudslides from heavy rain tin can cause problems in whatever mountainous area, particularly the Southwest. Large stretches of desert shrub in the west can fuel the spread of wildfires. The narrow canyons of many mountain areas in the west and severe thunderstorm action during the summertime atomic number 82 to sometimes devastating flash floods besides, while nor'easter snowstorms can bring activity to a halt throughout the Northeast (although heavy snowstorms can occur almost anywhere).
Geologic [edit]
The West Coast of the continental United States makes upwards part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area of heavy tectonic and volcanic action that is the source of 90% of the world's earthquakes.[ citation needed ] The American Northwest sees the highest concentration of active volcanoes in the The states, in Washington, Oregon and northern California forth the Cascade Mountains. There are several agile volcanoes located in the islands of Hawaii, including Kilauea in ongoing eruption since 1983, but they do not typically adversely touch on the inhabitants of the islands. There has non been a major life-threatening eruption on the Hawaiian islands since the 17th century. Volcanic eruptions tin can occasionally be devastating, such as in the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in Washington.
The Band of Fire makes California and southern Alaska particularly vulnerable to earthquakes. Earthquakes tin can cause extensive damage, such as the 1906 San Francisco earthquake or the 1964 Adept Friday earthquake most Anchorage, Alaska. California is well known for seismic activity, and requires large structures to be earthquake resistant to minimize loss of life and holding.[27] Exterior of devastating earthquakes, California experiences small-scale earthquakes on a regular footing.
At that place have been about 100 significant earthquakes annually from 2010 to 2012. Past averages were 21 a year. This is believed to be due to the deep disposal of wastewater from fracking. None has exceeded a magnitude of 5.6, and no i has been killed.[28]
Other natural disasters [edit]
Other natural disasters include: tsunamis effectually Pacific Bowl, mud slides in California, and wood fires in the western half of the contiguous U.South. Although drought is relatively rare, information technology has occasionally caused major economic and social disruption, such equally during the Grit Basin (1931–1942), which resulted in widespread ingather failures and dust storms, beginning in the southern Bang-up Plains and reaching to the Atlantic Ocean.
Public lands [edit]

Exclusive economic zones of the Usa, including insular areas
The United States holds many areas for the utilize and enjoyment of the public. These include national parks, national monuments, national forests, wilderness areas, and other areas. For lists of areas, come across the following manufactures:
- List of National Parks of the United States
- List of National Natural Landmarks
- List of U.S. National Forests
- Listing of U.S. Wilderness Areas
Human [edit]
In terms of human geography, the United States is inhabited by a various set of ethnicities and cultures. 65% of residents are white Christians, while the residual include Jews, Muslims, Hindus and black people.
Encounter also [edit]
![]() Usa portal
Usa portal
Notes [edit]
- ^ Areas not on the map: Aleutian Islands (Alaska); Northwest Hawaiian Islands (Hawaii); Mona Isle (Puerto Rico); Rota and Northern Islands Municipality (Northern Mariana Islands); Manu'a Islands, Rose Atoll and Swains Isle (American Samoa) and the U.S. Pocket-size Outlying Islands
- ^ The United States has a maritime border with the United Kingdom because the U.South. Virgin Islands borders the British Virgin Islands.[2] Puerto Rico has a maritime border with the Dominican Republic.[3] American Samoa has a maritime border with the Cook Islands (see Cook Islands–United States Maritime Purlieus Treaty).[iv] [5] American Samoa also has maritime borders with independent Samoa and Niue.[6]
- ^ One island in American Samoa (Swains Isle) is not in the Samoan Islands — it is in the Tokelau island chain.
References [edit]
- ^ U.Due south. State Department, Common Core Document to U.Due north. Commission on Man Rights, Dec 30, 2011, Particular 22, 27, fourscore; Homeland Security Public Law 107-296 Sec.two.(16)(A); Presidential Proclamation of national jurisdiction [i]
- ^ https://www.britannica.com/identify/United-States-Virgin-Islands. Britannica.com. U.s. Virgin Islands. Retrieved July three, 2020. Archived Apr 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ https://www.britannica.com/identify/Puerto-RicoBritannica.com. Puerto Rico. Retrieved July iii, 2020. Archived July 2, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Anderson, Ewan Due west. (2003). International Boundaries: A Geopolitical Atlas. Routledge: New York. ISBN 9781579583750; OCLC 54061586
- ^ Charney, Jonathan I., David A. Colson, Robert West. Smith. (2005). International Maritime Boundaries, 5 vols. Hotei Publishing: Leiden.
- ^ http://www.pacgeo.org/static/maritimeboundaries/Pacgeo.org. Maritime Boundaries. Retrieved July 3, 2020. Archived July 31, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "United States". The World Factbook. CIA. September thirty, 2009. Retrieved January 5, 2010.
- ^ "Population by Sex, Charge per unit of Population Increase, Surface Area and Density" (PDF). Demographic Yearbook 2005. United nations Statistics Sectionalisation. Retrieved March 25, 2008.
- ^ "United states". Encyclopædia Britannica . Retrieved March 25, 2008.
- ^ Countries of the World: 21 Years of Earth Facts, geographic.org, retrieved August 17, 2008
- ^ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-globe-factbook/graphics/ref_maps/physical/pdf/standard_time_zones_of_the_world.pdf Archived January eight, 2018, at the Wayback Auto CIA World Factbook - Standard Time Zones of the World, May 2018. (Map of the world showing the location of the contiguous U.S., Alaska, Hawaii, and the U.S. territories. Territories south of the "0" horizontal line (the equator) are in the southern hemisphere). Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ Murray, N.J.; Phinn, Southward.R.; DeWitt, One thousand.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. (2019). "The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats". Nature. 565 (7738): 222–225. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0805-8. PMID 30568300. S2CID 56481043.
- ^ "Managing Upland Forests of the Midsouth". U.s.a. Forestry Service. Archived from the original on October 17, 2007. Retrieved October thirteen, 2007.
- ^ "A Tapestry of Fourth dimension and Terrain: The Union of Two Maps - Geology and Topography". United states Geological Survey. Archived from the original on May fifteen, 2006. Retrieved October 13, 2007.
- ^ "USGS National Elevation Dataset (NED) ane meter Downloadable Data Drove from The National Map 3D Elevation Program (3DEP) - National Geospatial Data Asset (NGDA) National Meridian Data Set (NED)". United States Geological Survey. September 21, 2015. Archived from the original on March 25, 2019. Retrieved September 22, 2015.
- ^ "Physiographic Regions". U.s. Geological Survey. April 17, 2003. Archived from the original on May xv, 2006. Retrieved January xxx, 2008.
- ^ Williams, Jack Each state's low temperature tape, USA today, URL accessed 13 June 2006.
- ^ "Atmospheric condition and Climate" (PDF). Official website for Expiry Valley National Park. National Park Service U. South. Department of the Interior. January 2002. pp. 1–2. Retrieved October 5, 2006.
- ^ "WMO Printing release No. 956". World Meteorological Organization. September 13, 2012. Archived from the original on Apr 6, 2016. Retrieved April x, 2016.
- ^ a b Lonely Planet. "Rainmaker Mountain in Tutuila". Solitary Planet. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017. Retrieved September ane, 2019.
- ^ National Atlas, Boilerplate Annual Atmospheric precipitation, 1961-1990 Archived 2006-09-28 at the Wayback Machine, URL accessed 15 June 2006.
- ^ "ScholarSpace at University of Hawaii at Manoa: Climatology of Haleakalā". R.J. Longman and T.W. Giambelluca. Climatology of Haleakala. Climatology of Haleakalā Technical Study No. 193. Volume one, Event 1. Pages 105-106. 2015. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ Hereford, Richard, et al., Precipitation History of the Mojave Desert Region, 1893–2001, U.South. Geological Survey, Fact Canvass 117-03, URL accessed xiii June 2006.
- ^ NOVA, Tornado Sky, Hunt for the Supertwister, URL accessed 15 June 2006.
- ^ O'Connor, Jim E. and John Eastward. Costa, Large Floods in the United States: Where Thley Happen and Why, U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1245, URL accessed 13 June 2006.
- ^ NSSL: Severe Atmospheric condition 101 Archived 2012-03-twenty at the Wayback Machine. Nssl.noaa.gov. Retrieved on 2013-07-29.
- ^ "Building Safer Structures". Archived from the original on May 11, 2010.
- ^ Vergano, Dan (July 12, 2013). "Study:Earthquake increase tied to energy boom". The Burlington Costless Printing. Burlington, Vermont. pp. 10A. Retrieved July 14, 2013.
Further reading [edit]
- Brown, Ralph Hall, Historical Geography of the Us, New York : Harcourt, Brace, 1948
- Stein, Marker, How united states Got Their Shapes, New York : Smithsonian Books/Collins, 2008. ISBN 978-0-06-143138-8
External links [edit]
- USGS: Tapestry of Time and Terrain
- United states of america Geological Survey - Maintains free aeriform maps
- National Atlas of the U.s.
Coordinates: 38°00′00″N 97°00′00″W / 38.000°N 97.000°W / 38.000; -97.000
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_the_United_States
0 Response to "What Natural Resources Can Be Found Outside of the United States?"
Postar um comentário